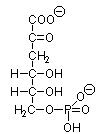CHEM-642 Biochemistry
Name ______________________________
Final Examination
7:00 – 10:00 PM, Monday, 21 May 2001
Part – I (100 Points)
Dr. White - Instructor
There are 9 pages to this half of the examination. Write
your name on each new page. Read every question so that you understand
what is being asked. If you feel any question is unclear or ambiguous,
clearly explain your answer or interpretation. Please call my attention
to any errors you encounter.
You will be given a separate page which has many
metabolic pathways written on it.
This examination will assess your learning, problem-solving
skills, and ability to communicate clearly. It is intended to be challenging
even to the best students in the class. Some of the questions will deal
with material you have not seen before and is not in your text; however,
they can be answered by applying basic principles discussed in the course.
Do not expose your answers to the scrutiny of your neighbors.
Please fold under each page before you go on to the next.
Breakdown of the examination by sections:
Short Answer
10 Points
Structures
16 Points
Multiple Choice
30 Points
Problems
20 Points (+5 Bonus)
Short Essays
24 Points
Total
100 Points
Exam (Part 1) Statistics: N = 49 Average = 51.5
Range 18 - 84
Part I - Short Answer Questions (1 point each)
__________________________ 1. Another name for biosynthesis.
__________________________ 2. Coenzyme involved in transamination
reactions.
__________________________ 3. One letter symbol for tryptophan.
__________________________ 4. Dihydrofolate reductase
is inhibited by this antitumor agent.
__________________________ 5. Number of carbon atoms in
phosphoribosylpyrophosphate.
__________________________ 6. NAD is an abbreviation for.
__________________________ 7. Aspirin inhibits the synthesis
of this class of compounds.
__________________________ 8. Element common in nucleic
acids and infrequent in proteins.
__________________________ 9. Common abbreviation for
adenylic acid..
__________________________ 10. Group of organisms that
excrete nitrogen as uric acid.
Part II Structures (16 points)
1. (8 Points) During protein
synthesis, tRNAs go through a cycle in which they become aminoacylated
at their 3' -CCA end with their cognate amino acid, bind to the A-site
on the ribosome, undergo a transpeptidation reaction to form a peptidyl
tRNA, translocate to the P-site, transfer the peptidyl moiety to the next
aminoacyl tRNA, and then dissociate to repeat the cycle. Consider a tRNATyr
participating in normal protein synthesis and bearing a dipeptide on its
2’ hydroxyl group. Draw the complete structure of the expected dipeptide
attached to the tRNATyr.
2. (8 Points) Draw the structure of the terminal
3' dinucleotide (-CA) at the end of tRNATyr and show where and
how the dipeptide above is covalently attached to it.
Part III Multiple Choice (3 points each, 30 points
total)
____ 1. Which of the following groups of three
amino acids consist
only of amino acids we cannot synthesize from
simple precursors and must obtain from our diet?
A. G, C, L B. F, K, V
C. E, T, H D. M, R,
Q
E. N, P, D F. I,
Y, S
_____ 2. Consider Question 1 again and the same
set of choices. Which group of amino acids consists only of amino
acid we can synthesize?
_____ 3. Consider the following isotopes some of
which are used as metabolic tracers. Which group consists only
of non-radioactive isotopes?
A. 18O, 35S, 3H
B. 14C, 16O, 14N
C. 13C, 32P, 2H
D. 12C, 3H, 15N
E. 31P, 2H, 14N
_____ 4. The X and Y columns pair components of
fatty acid synthesis with components of protein synthesis, respectively.
Examine each pair. Which pair has the relationship, X is to fatty acid
synthesis as Y is to protein synthesis?
|
|
X
(fatty acid synthesis)
|
Y
(protein synthesis)
|
| A. |
Malonyl CoA |
Ribosome |
| B. |
Coenzyme A |
tRNA |
| C. |
NADPH |
Met-tRNAfMet |
| D. |
ATP |
GTP |
| E. |
Acetyl CoA |
mRNA |
| F. |
Fatty Acid Synthase |
ATP |
_____ 5. Which statement is false?
A. B-complex vitamins are
precursors for a variety of coenzymes.
B. Fatty acids found in plants and
animals have predominantly 16 or 18 carbon atoms.
C. Some coenzymes are also nucleotides.
D. The a
-helix is an important part of the structure of DNA.
E. Galactose is the 4-epimer of glucose.
F. Steriod biosynthesis from acetyl
CoA starts in the cytosol .
_____ 6. Which statement is true?
A. TPP stands for thymine pyrophosphate
B. Humans can convert fatty acids into
glucose.
C. Adenylate Energy Charge can never
be higher than 1.0.
D. Both CO2 molecules generated
with each turn of the TCA cycle come directly from the
acetyl group that
enters the cycle.
E. Mutated enzymes with impaired activity
would have low sensitivity coefficients.
F. Dehydration reactions use NAD.
_____ 7. An aldolase reaction in bacteria cleaves
the compound below. What are the products of this reaction?
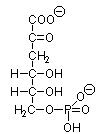 |
A. Pyruvate
+ Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
B. Carbon Dioxide + Ribose-5-Phosphate
C. 3-Phosphoglycerate + Propionate
D. Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
+ Dihydroxyacetone
Phosphate
E. Dihydroxyacetone + 3-Phosphoglycerate
F. Acetate + Erythrose-4-Phosphate |
_____ 8. Considering all of the reactions
and compounds that use or incorporate nucleotides in a cell, which of the
following bases would be least concentrated in a total
cell hydrolysate?
A. Adenine
B. Guanine C.
Cytosine D. Thymine
E. Uracil
_____ 9. Alpha–ketobutyrate is an intermediate in
the catabolism of methionine. The carbons from methionine enter the Citric
Acid Cycle at:
A. SuccinylCoA B.
alpha-ketoglutarate
C. Fumarate D. Citrate
E. Oxaloacetate
_____ 10. The Cori Cycle is a cooperative venture
between muscle and liver, with the blood stream linking these two tissues.
Select the statement that is FALSE about the Cori Cycle.
A. It operates principally
when muscle is actively working, not in the resting state.
B. In muscle, glycolysis is occurring,
while in liver gluconeogenesis is occurring.
C. The blood transports glucose from
muscle to liver. It then transports lactate
from liver
back to muscle.
D. Lactate dehydrogenase operates in
the direction, pyruvate to lactate, in muscle,
whereas in
liver this enzyme operates in the direction, lactate to pyruvate.
E. The Cori Cycle operates at the expense
of ATP in the liver.
Part IV – Short Problems
1. Consider the bacteria, Youdea
hulliheni, that normally oxidizes glucose by the Embden-Meyerhof Glycolytic
pathway, but, due to a mutation in the gene for phosphoglucose isomerase
(the aldo-keto isomerase that interconverts G6P and F6P), must use the
pentose phosphate pathway as a detour around the metabolic block as shown
below. The cofactors for the individual enzymes are omitted but you will
need to know them.
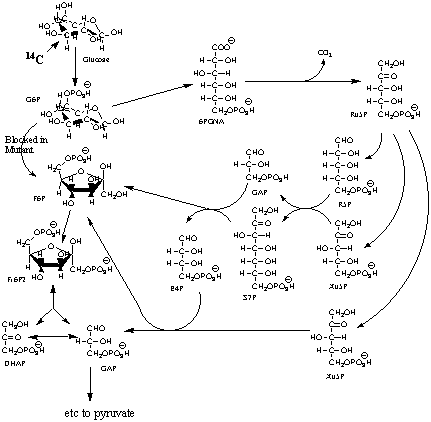
____ ATP
____ NAD(P)H |
A. (4 points)
In this modified pathway for glucose oxidation, five, rather than six,
glyceraldehyde-3-Ps (GAP) are produced per three glucoses. Calculate the
net production of ATP and NAD(P)H per glucose in going from glucose
to pyruvate in this pathway. (Use the back of this page as a work sheet
if necessary for this and subsequent questions.) |
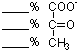
|
B. (6 points) If carbon 3 of glucose
were labeled with 14C, how would the label be distributed in
pyruvate? |
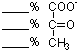 |
C. (3 points) How would the 14C
label be distributed in pyruvate, if the normal glycolytic pathway were
operating alone, i. e. phosphoglucose isomerase is fully functional and
the pentose phosphate pathway were not involved. |
2. The biosynthesis of phenylalanine
requires erythrose-4-P (E4P) and two moles of phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP)
as precursors as is shown below. Return to Question 1 and the metabolism
of [3-14C] glucose in the bacteria lacking phosphoglucose isomerase.
A. (7 points) Trace the labeled
carbons and show which carbons of phenylalanine would be labeled. (Because
the answer here is dependent on your answer on 3B, I will give up to 6
points for an answer that is consistent with an incorrect answer to 1B.)
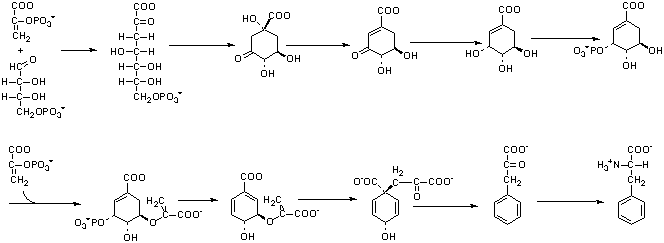
B. Bonus Question (5 points)
Do not do this until you have completed the rest of the examination. What
would be the relative amounts of
14C in each of the labeled
carbons of phenylalanine?
Part V - Essay Questions (8 Points each) Writing
reflects how you think. Among the "right answers" I will read for the following
questions, some will be better than others because they show greater depth
of understanding, avoid extraneous or inaccurate information, provide a
more logical structure, use appropriate examples, and select words with
precision. Better quality answers will receive higher marks. Therefore,
organize your thoughts before you write.
1. Discuss the regulation of the branched
purine biosynthetic pathway or the aspartate family of amino
acids. Answer only one of the two choices.
2. Explain the following: A man on a
low protein – high carbohydrate excretes 6.2 grams of urea per day. Then,
after a three-day fast, he excretes 26.3 grams of urea per day or
the relation between metabolic energy sources and world record human running
performance at various distances. Answer only one of the two choices.
3. Suppose you are a bacterium
growing happily at 25° C and suddenly you
are transferred to a 37° C incubator which
causes a sharp increase in the fluidity of your cell membranes. Discuss
the compositional options you have to regain your original membrane fluidity?
Return to Department's
Home Page, Course
Home Page, Course
Syllabus.
Posted 15 June 2001 by Hal
White.
Copyright 2001, Harold B.
White, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Delaware,
Newark, DE 19716