CHEM-527 Introductory
Biochemistry
Problem No. 1b
Aspartate Transcarbamylase Quaternary
Structure
from the work of Howard
Schachman
1. The enzyme aspartate transcarbamylase (ATCase) catalyzes
the first committed step in pyrimidine biosynthesis. What is the reaction
catalyzed by ATCase?
2. Native ATCase is a dodecamer (R6C6)
composed of six regulatory (R) subunits and six catalytic (C) subunits.
The researchers in Dr. Schachman's laboratory wanted to figure out the
quaternary structure of the complex by distinguishing between stronger
and weaker subunit interactions. Under mild conditions they were
able to partially dissociate the complex into smaller aggregates containing
only R or C subunits. They could separate the two classes of subunit
aggregates and then recombined them to reform active dodecameric enzyme.
In addition, they reacted the native enzyme with succinic anhydride which
succinylates the epsilon-amino groups of lysine residues and creates a
modified but still active enzyme (R'6C'6) with a
substantial negative charge. By dissociating, isolating, and recombining
various combinations of modified and unmodified subunit complexes, they
generated various hybrid dodecameric enzymes and analyzed them by gel electrophoresis
(not SDS-PAGE) as diagrammed below. The dark spots represent ATCase activity
in the gel. The parentheses indicate combinations of native and modified
subunits summing to 6.
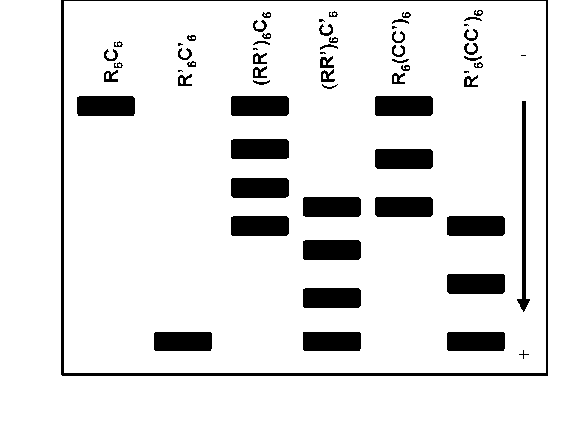
a. Explain the electrophoretic patterns observed in
terms of the subunit structure of ATCase.
Identify the subunit composition of each band shown above.
Is your explanation consistent.
b. Assume that the recombination of modified and unmodified
subunits occurs randomly. What are the relative amounts of ATCase
in each of the electrophoretic bands for (RR')6C and R6(CC')6
above?
Assume a binomial distribution and that prior to electrophoresis the native
and modified subunit aggregates were present in equal amounts. e.g. [Rn]
= [R'n].
c. Constraints of symmetry restrict the possible arrangements
R6C6 aggregates. X-ray crystallography of the enzyme
shows that each subunit is isomorphous with the other subunits of its type.
i.e. they are indistinguishable from each other since they fit into the
complex structurally identical ways. Draw a representation of E.coli
ATCase which satisfies the X-ray observations and is consistent with the
electrophoretic observations .
Return to CHEM-527
Home
Page,
Syllabus,
or Departmental Home Page.
Posted: 9 September 1999,
Revised 9/10/99 by Hal White
Copyright 1999, Department
of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Delaware, Newark, DE
19716