There are 9 pages to this examination. Put your name on each new page. If you feel any question is unclear or ambiguous, clearly explain your answer or interpretation.
Do not expose your answers to the scrutiny of your neighbors. Please fold under each page before you go on to the next.
Breakdown of the Exam by sections:
1. (8 Points) The data bases for protein amino acid sequences now contain several hundred thousand, perhaps more than a million, entries. Biochemists, with nothing better to do, have searched these data bases for cosmic (comic?) messages C words of profound meaning spelled out in the single letter amino acid sequence such as ELVIS and LIVES in the same protein. ELVIS has been found several times. Actually, ELVIS is a rather uninteresting peptide. What would be the covalent structure of a hexapeptide having the amino acid sequence DARWIN?
Bonus Point. Why won=t LINUS PAULING be found in the protein sequence data base?
2. (6 points) Draw the complete covalent structures and specifically name three biochemical compounds, a sugar, a lipid, and a nucleotide. You can chose any one you like in each category. (Because you have considerable choice here, no partial credit will be given to slightly inaccurate or incorrectly identified structures.)
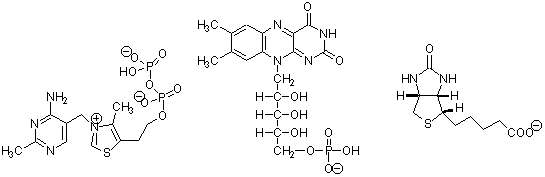
3. (6 points) Identify each of the coenzymes below and circle the site in each that is involved in covalent catalysis.

a. ___________________ b. __________________ c. _________________
Short Answer (20 points, 1 point each)
_______________________________ 1. Chemical bonds that stabilize the a-helix.
_______________________________ 2. Glutamate is to Aspartate as Leucine is to.
_______________________________ 3. Serine is to Threonine as Valine is to.
_______________________________ 4. Number of subunits in aspartate transcarbamoylase
_______________________________ 5. Vmax is not affected by this type of inhibitor.
_______________________________ 6. Type of inhibitor whose Ki is significantly lower than the Km for the substrate.
_______________________________ 7. Colored, iron-containing prosthetic group covalently attached to cytochrome c.
_______________________________ 8. Nucleophilic amino acid residue involved covalently in the catalytic mechanism of trypsin.
_______________________________ 9. General term for inactive enzyme precursors such as trypsinogen.
_______________________________ 10. Name of the first enzyme to be crystallized.
_______________________________ 11. Substance that gives raw egg white a faint yellow color.
_______________________________ 12. Niacin is a precursor to this coenzyme.
_______________________________ 13. Glucose is to fructose as glyceraldehyde is to:
_______________________________ 14. Metal ion involved in the urease active site.
_______________________________ 15. Membrane lipid not hydrolyzed by strong acid.
_______________________________ 16. Coenzyme associated with a variety of reactions involving amino acids.
_______________________________ 17. Plant pigment derived from tryptophan.
_______________________________ 18. Hexose that is also a vitamin.
_______________________________ 19. Riboflavin is to FAD as pantothenate is to.
_______________________________ 20. The number of H-bonds per H2O in ice.
Bonus point. Name the chemist who won two unshared Nobel
Prizes including the Peace Prize?
Multiple Choice Questions (30 points, 3 points each)
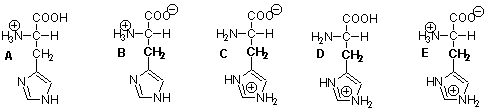
____ 1. Pick the predominant ionic form of histidine expected
at pH 4. The pKa of the imidazole moiety is 6.0.
____2. Which of the following atoms might be absent from a purified protein.
A. For many proteins, the primary amino acid sequence determines the tertiary structure.
B. In evolution, primary structure is more highly conserved than tertiary structure.
C. The tertiary structure of hemoglobin is dominated by a-helices.
____4. Identify the treatment that would be inappropriate for the purification of a protein.
____ 5. If doubling the substrate concentration results in more than a two-fold increase in reaction velocity of an enzyme, one could conclude that
A. the substrate is an allosteric modifier of enzyme activity.
B. the enzyme probably is monomeric.
C. the enzyme obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
D. the enzyme is saturated.
E. the substrate
is distorted during catalysis.
____ 6. Five enzymes that catalyze the reaction A Y B were found to have the following kinetic characteristics.
A. 100 1000
B. 1 10
C. 10 10
E. 10 100
A. Contain sulfur.
B. Are covalently attached to lysine in the enzymes that use them.
C. Can be synthesized by humans.
D. Contain nitrogen.
E. Participate
in decarboxylation reactions.
____ 8. Which one of the following does not involve the loss of water in its formation?
____ 9. Which of the following fatty acids would be most common in the membrane phospholipids of your body?
H H
A. CH3(CH2)11COO-
B. CH3(CH2)8COO-
C. CH3(CH2)7C=C(CH2)7COO-
____ 10. A biochemist treated half of a sample of
purified lactate dehydrogenase with succinic anhydride which derivatizes
the e-amino groups of lysines giving them negative
charges. She mixed the derivatized sample with the native protein under
conditions where the subunits could randomly dissociate and reassociate.
Finally, she subjected the mixture to electrophoresis and observed five
evenly spaced bands of protein. Based on this information, what can be
concluded about the quaternary structure of lactate dehydrogenase.
A. It is a pentamer of identical subunits
B. It is normally monomeric but succinylation causes aggregation
C. Dimers and trimers associate to give pentamers
D. It is a tetramer of similar or identical subunits
E. There is
insufficient information to deduce a structure
Thought Questions and Short Essays (30 points)
1. (6 points) Humans sweat to maintain their body temperature;
however, sometimes it is more important to conserve water and endure a
day-time fever on hot days as camels do in arid climates. Estimate
how many liters of water a 500 kg camel would conserve by allowing its
temperature to rise 6 degrees C. The specific heat of water is 1 cal/g
C. Its heat of vaporization is 540 cal/g.
2. In attempting to synthesize the C-terminal peptide of the hormone gastrin, James Schlatter serendipidously discovered the sweetener Aspartame. Not so sweet is the N-terminous of gastrin where 5-oxo-proline is found. (Oxo means a carbonyl oxygen.)
a. (3 points) Draw the structure of 5-oxo-proline.
b. (3 points)
What amino acid (not proline) is the precursor of 5-oxo-proline via a dehydration
reaction?
3. Branched polysaccharides are common in bacterial cell walls. Mycobacterium tuberculosus has a complex cell wall that includes polymers of a-D-galactofuranose.
a. (3 points) Draw the structure of a-D-galactopyranose.
b. (3 points)
Draw the structure of a-D-galactofuranose.
4. (4 points) Hemoglobin is a tetramer with an a2b2
structure. Each subunit is very similar to the tertiary structure of myoglobin.
However, a number of hydrophilic amino acid residues in the myoglobin structure
have been replaced with hydrophobic residues in the hemoglobin subunits.
Provide a reasonable explanation for this observation.
5. (8 points) While you are having dinner with a health-conscious
aunt, she washes down a huge vitamin pill with fanfare and offers you one.
Your skeptical uncle, who has been through this show many times before,
cuttingly says, AYou might as
well flush them down the toilet because that=s
where they all end up anyway.@
Shortly thereafter, you get sucked into the middle of a ritual family battle
when your aunt, knowing you are taking a biochemistry course, seeks your
support. ATell him what vitamins
are and why they are they important,@
she demands. Without taking sides, what information could you provide?
6. Bonus Thought Question (6 points) The last of the dinosaurs
perished 65 million years ago in the aftermath of an asteroid collision
with the earth near the present-day Yucatan Peninsula. While there are
some rather well preserved fossils of dinosaurs, none of them so far contain
preserved proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, or other biochemical molecules
of interest. If some day a biochemist claims to have cloned DNA from a
dinosaur bone and, from it, deduced the sequence a protein such as cytochrome
c, would there be any way that you could decide that it was from a dinosaur
and not from a modern organism? Please explain your reasoning.